What can I find in this article?
- Emerald Colors
- Emerald Species
- Emerald clarity
- Emerald meaning
- Emerald healing properties
- Emerald prices
- Emerald Discovery
- Where are Emeralds found?
- Can emeralds be treated?
- What jewelry is emerald suitable for?
- Did you know? Interesting facts about emerald
- How emerald is formed?
- How to care for emerald
- How do you know if you have a real emerald?
- What is so special about emerald?
- Can I wear cracked emerald? Will an Emerald break if dropped?
- Emerald - Gemological Properties
Emerald Gemstone Information
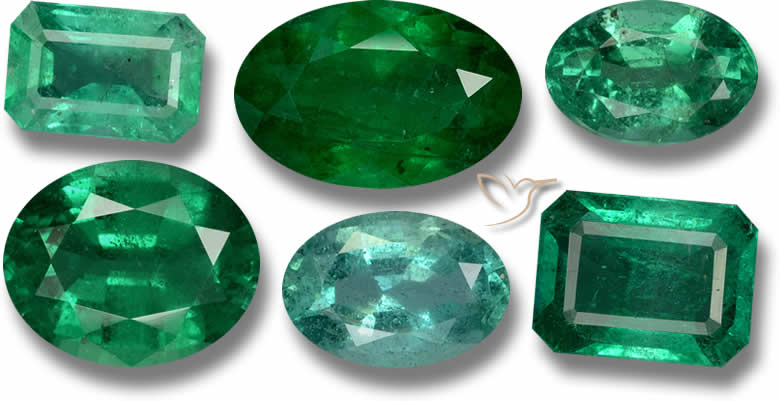

Introduction
Written many centuries ago, the Vedas, the religious texts of ancient India, say the following about Emeralds and their healing properties: 'Emeralds promise good luck' and 'the emerald enhances the well-being'. No wonder the treasure chests of Indian royalty were full of these gorgeous gems.
Emerald is the green to greenish blue gemstone of the mineral species beryl, the green is caused by the presence of chromium, vanadium or iron (or any combination of those three elements) and includes aquamarine and other colored beryl.
To be a true emerald, the gemstone has to be dark enough and saturated enough to be called emerald, if the color is considered too light then it will simply be a green beryl. The degree of greenness has led to a number of differing opinions of whether a stone can truly be called an emerald.
The most prized emeralds have a pure green color with a vivid color saturation that is evenly distributed throughout the stone with no visible color variations.
If the hue tends to be too blue or too yellow it will not be an emerald but a different variety of beryl and will devalue.
Emeralds have been valued highly in antiquity with ancient Egyptians, Romans, Indians, Aztecs and Incas venerating this wonderful gemstone.
The name comes to us from the Greek word 'smaragdos' and the Latin 'smaragdus' meaning green gem and goes back further to the Sanskrit 'maragdam' and Persian 'zumurrad' meaning emerald.

All emeralds are green, but only a particular intense green that is unequalled by anything else in nature can be a real emerald. The most expensive emeralds are evaluated by three categories, hue, tonal grade and saturation. Hue refers to the type of green the emerald has; bluish green, yellowish green and so on. Tonal grade decides the level of lightness or darkness and saturation is what gives the emerald its 'life', the vividness or sparkle of a great emerald and dullness or flatness of a lesser gem. In addition to color, the most-prized emeralds are highly transparent.
Emeralds can be divided into varieties or types rather than species. Emeralds are sometimes differentiated by their place of origin or the presence of certain impurities. Some of the better known emeralds include;
- Colombian Emeralds
- Colombian emeralds are mined in Colombia. These emeralds are the most highly valued.
- Brazilian Emeralds
- Brazilian emeralds are commonly lighter green gemstones than those mined in Colombia. The term "Brazilian emerald" sometimes refers to green tourmalines.
- Zambian Emeralds
- The high end market was slow to accept Zambian emeralds, but that began to change when Tiffany & Co. began to promote emeralds from Zambia in 1989. Today Zambian emeralds are well-respected and recognized for their own distinctive characteristics.
- Cat's Eye Emeralds
- These emeralds have a cat's eye effect, called a chatoyancy, which looks like a wide slit similar to the pupil in a cat's eye. Cat's eye emeralds are very rare and only found in paler green emeralds.
- Trapiche Emeralds
- The rarest type of emerald is the Trapiche Emerald, a very unusual combination of emerald and lutite. Because of the hexagonal structure of the emerald the two minerals alternate somewhat like the spokes on a wheel and result in a very unique formation. The only known source had been Colombia and the local name comes from its similarity to the rollers of a mill that would extract the juice from sugar cane - a trapiche. There have been some reports of examples recently found in Madagascar and Brazil and some unusual cases where the emerald forms the spokes rather than the other way round.
Gemstone clarity refers to the presence or non-presence of inclusions within the stone. Inclusions are any material such as minerals, gases, liquids or even other crystals trapped inside during its formation.
Of the four top gemstones, the others being diamond, sapphire and ruby, emeralds are unique in the number of high quality specimens containing inclusions, a flawless emerald is almost impossible to find. In fact it is the flaws that often give the emerald its charm and the lack of any inclusions is often a sign of a fraudulent stone.
In emeralds, just as in other colored stones, clarity and transparency are closely linked.
It is generally accepted that emeralds will have inclusions visible to the naked eye but only when it affects the transparency will it reduce the price.
Valuable emeralds with inclusions are so standard that there is even a name for them, Jardin emeralds (jardin is French for garden and is so named for its mossy or grassy appearance). When selecting an emerald, the inclusions to be wary of are ones that reach the surface of the gemstone as this can indicate future cracking or breaking.

Emeralds have been desired by man since the dawn of human civilization so it is not surprising that they should have a deep spiritual meaning. The ancient Romans associated the emerald with the goddess, Venus so the gems are said to bring passion, joy and unconditional love. If two lovers give each other an emerald their love will grow and become everlasting. Being green, the emerald also represents fertility, new growth, youth, vitality and the season of spring.
The emerald is also known for its association with vision, both the physical ability to see, as well as intuition and the psychic ability to foretell future events. Furthermore, emerald is regarded as a gemstone of wisdom that can enhance memory and mental acuity. Through a combination of intelligence and insight, it connects the unconscious and conscious mind, a process that opens up psychic powers of clairvoyance.
Emerald is known to combat aging by rejuvenating and revitalizing debilitated organs. Its connection to the heart is physical, as well as spiritual, and it is known to treat cardiac weakness. Moreover, emerald can be useful in treating ailments and conditions of the lungs, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, and kidneys, as well as the musculoskeletal system.
The May birthstone is best known throughout the ages as the quintessential gemstone for treating the eyes and restoring eyesight. Strained eyes can be soothed by a bath of emerald water, while the same concoction can alleviate eye infections. Drinking such an elixir is excellent for treating gout and strengthening memory.
There is an immense host of illnesses that may be treated by the use of emerald as a healing gemstone. These include cancer, colic, epilepsy, high blood pressure, skin disorders, syphilis, dysentery, vomiting, indigestion, asthma and anemia. There was a time when emerald was highly prized as an antidote to poisoning. In fact, even today there are Chinese folk healers using the powder of poorer quality emeralds to concoct their medicines.
Emerald's effect on intellect and memory provide one with the ability to speak eloquently. Moreover, holding a natural emerald for just 5 minutes a day can give one the power to rapidly recall facts. Overall, emerald is a great crystal for the workplace, as it nurtures balance, harmony and cooperation.
Finally, emerald has the ability to relieve any heaviness in our auric field by dissipating the negative energy that creates destructive patterns of behavior, and nourishing us with hope, encouragement, gentleness and prosperity. For those who have suffered a heart break it is especially useful, as it empowers people to rise above such adversity, and to see beyond into a future of love, vitality and compassion.
Disclaimer: Metaphysical and Alternative Crystal Healing Powers and Properties are not to be taken as confirmed advice. Traditional, Ceremonial and Mythological Gemstone Lore is collected from various resources and does not represent the sole opinion of SETT Co., Ltd. This information is not to replace the advice of your doctor. Should you have any medical conditions, please see a licensed medical practitioner. GemSelect does not guarantee any claims or statements of healing or astrological birthstone powers and cannot be held liable under any circumstances.
Emerald Price List |
||
|
Color |
Weight range |
Price range / USD |
|---|---|---|
|
Green |
1 - 2ct |
$80 - $1,500/ct |
|
Green |
2ct + |
$80 - $3,500/ct |
The emerald is one of the world's most valuable gemstones, and is extremely rare so can demand an exceptional price. As with all colored gemstones, the 4 Cs (color, clarity, cut and carat) determine the value but emeralds are priced in a slightly different way to other gemstones in that some inclusions are expected. Color is possibly the most important factor in valuing emeralds, they have a unique color, exclusive to natural emeralds. The color is further broken into hue; the exact color, tone; the lightness to darkness, and the saturation or vividness of the green color.
In top value emeralds, the hue will be green, without additional color undertones, the tone will be vivid and deep, not too dark or light and the saturation will be even throughout.
Emeralds can be cut into almost any shape with round and the octagonal 'emerald' cut being the most popular. Any cut which shows off the gem's natural color and sparkle will enhance its price.
The final indicator for price is, of course, the size of the emerald. Large carat sizes are particularly rare so a three carat emerald gemstone is not just three times the price of a single carat stone, more likely six times the price.

An additional price gauge can be the source of the emeralds. Emeralds are mined throughout the world but three sources provide the bulk of the premium gemstones.
The emerald stones from Colombia are valued the highest with those from Zambia and Brazil just behind.
Emerald gemstones are bought for their beauty, mystery and emotional attraction but they can also be a smart investment. Because of the rarity of large cut quality emeralds future prices are only expected to go up. Many investors are buying high quality emeralds to increase and maintain the value of their portfolios. If you are thinking of buying an emerald as a financial venture, get some good advice beforehand.
Emeralds are extraordinarily profitable, and like other gems easy to store and conceal. An emerald worth millions of dollars could be less than 4 inches long and easily fit in your hand. The price ceiling for high quality emeralds can reach $90,000 per carat for outstanding examples. It is understandable how a one ounce fine Colombian emerald crystal could fetch millions at the current price levels.
Emeralds may well have a history as long as that of civilized man, they are certainly ancient gemstones. The oldest book in the world, the Papyrus Prisse, which is around 4000 years old, says at one point, "But good words are more difficult to find than the emerald, for it is by slaves that it is discovered among the rocks."
The quote probably refers to the mines located near Luxor where tools dating back to 1300 B.C., during the reign of Ramesses II, have been found. Other ancient mines include Muzo, Chivor and Cosquez in Colombia and Mingora in Pakistan where gems were mined 2500 years ago.
Throughout known history they have been revered by civilizations across the world from the Babylonians who wrote about their sales in the markets, to Aristotle who recommended the wearing of one, to Nero who had sunglasses made from emeralds, to the Incas who worshipped Umina, a goddess represented by an emerald the size of an ostrich egg!
Emerald is derived from a Persian word', zumurrad', meaning "green gem". This progressed to the Greek word, 'smaragdos' then to Latin as smaragdus, sometimes esmeraude or esmeralde, and in the 16th century, to the French, esmeralde and on to the English, emerald.
Emeralds are mined throughout the world (Pakistan, Afghanistan, Russia, Australia, the United States) but Colombia, Brazil and Zambia are the three major sources. Colombia, located on the continent of South America, arguably produces the finest of all emeralds and produces 70-90% of the emeralds for the global market.

Unlike most gemstones, emeralds, are never exposed to traditional heat treatment to alter their color or enhance their clarity however this does not mean they are not treated in any way.
Most emeralds are not flawless and have numerous internal inclusions and fractures and also tiny surface breaking crevices or cracks. For this reason, the vast majority of emeralds are treated with oils, usually cedar, to improve their clarity.
Cedar oil is tacky and thick, so it is not easy for it to penetrate the microscopic cracks in emerald. It therefore requires some heat to warm the oil and pressure to force the oil into the fissures. First the emeralds are cleaned in an acid bath, then the gems are isolated in tanks together with pure cedar oil and locked tight. The heat liquefies the cedar oil and the pressure helps it penetrate any tiny cracks in the emerald.
The emeralds are left to cool and the oil returns to its viscous state, remaining within the emerald and improving its clarity and transparency. The stones are then removed and cleaned. Eventually the emerald will need re-oiling and re-cleaning to keep it in the best possible condition.

Mohs Hardness Scale is used as a convenient way of comparing the scratch resistance of minerals developed by German geologist Friedrich Mohs in the early 1800s. Minerals are rated according to their resistance to being scratched by some common materials, for example a fingernail, a copper coin, a steel nail. The scale rates substances such as talc at the bottom with a rating of 1 and diamonds at the top with a maximum rating of 10. Emeralds are rated at 7.5 to 8, towards the top of the scale, making them hard enough for all types of jewelry.
See our detailed article on the Mohs Scale here
With emeralds, the cut should emphasize the color of the stone, rather than its brilliance. Symmetrical, open and uniform facets are ideal to promote the color and sparkle of emeralds. One of the most traditional cuts for an emerald is the emerald cut. This cut has large open facets, which enhances the color and size of the emerald. It also reduces the waste that often occurs when cutting fine gems.
This beautiful gemstone makes stunning jewelry pieces but we would suggest open settings wherever possible to show off the gems natural fire and brilliance. For rings and pendants, designs that allow for light to pass through will maximize transparency and the truncated design of an emerald-cut reduces the risk of corners and edges chipping.
When storing emeralds avoid keeping them with other harder gemstones which may scratch their surface.
- Emerald is the birthstone for May
- its green color conjures up images of spring, re-growth and fertility. It symbolizes love and faithfulness so would make an ideal gift for a loved one who celebrates a birthday in May. According to tradition, emeralds represent pure, true love - and change color when the loved one is unfaithful.
- Emeralds were used as trade currency
- The Spanish traded emeralds across Europe and Asia for precious metals, which opened up the emerald trade to the rest of the world.
- Emerald is a wedding anniversary gem
- It is also the gemstone that celebrates the 20th and the 35th wedding anniversary and who would not want an emerald on those special days?
- Top quality emeralds can be worth more than diamonds on a per-carat basis.
- The oldest emeralds are about 3 billion years old.
- A 1-carat emerald appears larger than a 1-carat diamond because of their lower density.
- Spanish Conquistadors plundered Incan emeralds
- As gifts to the goddess Umina, the people of the Peruvian city of Manta would offer up emeralds to her. When Spanish conquistadors arrived they seized the immense horde of gemstones and believing true emeralds to be unbreakable tested them by smashing them on anvils! They took vast quantities back to Spain and eventually discovered and took over the mines at Chivor and Muzo in Colombia which still produce the world's finest emeralds to this day.
- An emerald pendant necklace owned by Elizabeth Taylor sold for $6.5 million in 2011, that is about $280,000 per carat!
- The Duke of Devonshire Emerald is one of the largest uncut emeralds weighing 1,383.93 carats.
- The emerald was Cleopatra's favorite gemstone, and her passion for it was well documented.
Princess Katharina Henckel von Donnersmarck's Emerald and Diamond Tiara
This tiara is made up of eleven rare Colombian pear-shaped emerald gemstones which were supposed to have been once owned by Emperor Napoleon III's wife, Eugenie. The tiara was commissioned by a German prince for wife, Katharina, and was sold at a Sotheby's for $12.7 million.
Emerald is a crystal made from the mineral called beryl which forms in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks, produced by heat and pressure. Emeralds are made from 4 elements, beryllium, aluminum, silicon, and oxygen that are found deep in the Earth's crust: These elements are found flowing in seams in this crust filled with hot water called hydrothermal veins. When the conditions are just right in these seams and they cool enough, emerald crystals start to form. Emerald is different from other kinds of beryl (such as aquamarine) by containing small amounts of the element chromium. The emeralds we mine today are the results of processes that occurred hundreds of millions of years ago.
Precious emerald is sensitive to pressure and vulnerable to household chemicals. Although emerald is one of the harder gemstones, it does still require careful handling, due to its naturally included and flawed formation. Extra care should be taken when handling emeralds as they are more fragile than other forms of beryl. Avoid wearing emerald jewelry when working with harsh chemicals or household cleaners, such as bleach or acid. When cleaning, you can use warm soapy water and a tissue or a soft cloth. Be sure to rinse the stones well to remove all soapy residue.
Avoid ultrasonic cleaners and steamers when cleaning your emeralds as these can remove the oils that are used to enhance the emeralds. Traditional oiling for emeralds is stable but not permanent, which means that most emeralds will need re-oiling every so often to return some of their lost color and luster. Always remove any emerald jewelry before exercising, cleaning, playing sports or engaging in vigorous physical activities. Emeralds can easily scratch other gems, and they can easily be scratched by harder gems such as topaz and sapphires. To prevent scratches store emeralds away from other gemstones and gemstone jewelry. Store your gemstones by wrapping them in soft cloth and placing them in a fabric-lined box.

To know for certain that an emerald is 100% real you need specialized gemology equipment or certificates from recognized authorities but there are a few techniques even the novice can apply. Use these techniques only as a guideline, to be sure, have your gemstone examined by a professional.
Look for flaws through a magnifying lens or jeweler's loupe. Examine the gem under magnification, ideally through a jeweler's loupe. Hold it so light strikes it at an angle, if you see tiny flaws or irregular patterns within the crystal, it is probably a real gem - although not necessarily an emerald. If your gem is very clear, with no inclusions, you can assume it is a fake.
Applying oil to an emerald will usually enhance its appearance but with a synthetic stone the clarity will not change.
Emeralds conduct heat very efficiently, so you could try a breath test. Breathe on the gemstone and observe the mist - on a real emerald the mist will disappear almost instantly but with a fake it will last 4 or 5 seconds.
When lit, real emeralds produce little to no "fire," or colorful flashes, if your gem produces a rainbow of flashes, it is not an emerald.
Examine the color. The mineral, beryl, is only called emerald if it is dark green or blue-green, too yellow or too light a green and it is just an ordinary beryl. The line between emerald and green beryl is hazy - jewelers often disagree over the classification of a gem.
Emeralds are relatively hard gemstones and whereas glass and other weak materials used in fake gemstones wear down quickly, emeralds will retain sharp clean edges on the facets. If the edges of the facets look soft and worn, the gem is likely fake.
Beware of cheap prices. If the deal seems too good to be true, trust your instincts. At GemSelect, we currently offer brief identification reports from your choice of two well-respected independent gemological laboratories, The Asian Institute of Gemological Sciences (AIGS) and Burapha Gemological Laboratory (BGL Lab).
As we have mentioned before, emeralds gemstones often contain inclusions - a perfectly clear stone is extremely rare. These inclusions are part of the emerald's charm but can be treated with oils or fillers. Over time these oils can leach out of the stones, this is quite normal but can make the gemstone more brittle and more likely to break. If you have noticed your emerald seems to be cloudier or duller than before, the stones can be re-oiled.
To the naked eye, both cracks and inclusions can look the same. But knowing where and how far to look can help you see the difference between the two. If you see an emerald that has inclusions only in its center far from any surface or corner it will not be likely to break but if the inclusions reach the surface of the gem this is a sign of potential future problems.
|
Chemical Formula: |
Al2Be3Si6O18 - Aluminum beryllium silicate |
|
Crystal Structure: |
Hexagonal; hexagonal prisms |
|
Color: |
Emerald green to green to slightly bluish or yellowish-green |
|
Hardness: |
7.5 to 8 on the Mohs scale |
|
Refractive Index: |
1.565 to 1.602 |
|
Density: |
2.67 to 2.78 |
|
Cleavage: |
Indistinct |
|
Transparency: |
Transparent to opaque |
|
Double Refraction or Birefringence: |
-0.006 |
|
Luster: |
Vitreous |
|
Fluorescence: |
Usually none |
- العربية | معلومات الزمرد - أحجار كريمة خضراء زاهية ذات جودة لا مثيل لها
- 中文 | 祖母绿信息 - 品质无与伦比的鲜绿色宝石
- Français | Informations sur l'émeraude - Pierres précieuses vertes vives ...
- Deutsch | Informationen zu Smaragden – Leuchtend grüne Edelsteine von unverg...
- Italiano | Informazioni sugli smeraldi - Pietre preziose verdi vivide di qual...
- 日本語 | エメラルドについて - 比類のない品質の鮮やかな緑色の宝石
- 한국인 | 에메랄드 정보 - 타의 추종을 불허하는 선명한 녹색 원석
- Português | Informação Esmeralda - Pedras preciosas verdes vivas de qualidade ...
- Pусский | Информация об изумрудах - Ярко-зеленые драгоценные камни непревзой...
- Español | Información de la esmeralda - Piedras preciosas de color verde viv...













